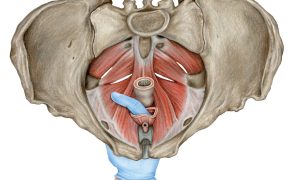
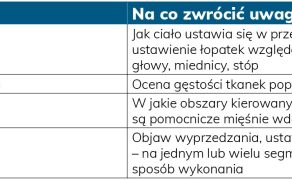
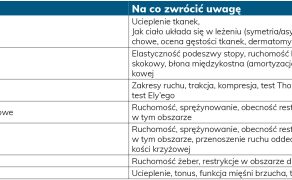
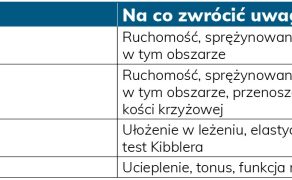
Podejście diagnostyczno-terapeutyczne do pacjentki z nietrzymaniem moczu
Elementy składowe terapii mięśni dna miednicy
- Edukacja ‒ pacjentka musi zrozumieć, jak funkcjonuje jej ciało.
- Nauka prawidłowych nawyków dnia codziennego.
- Praca nad prawidłową postawą ciała oraz reedukacja oddechowa.
- Nauka świadomości ciała
- Normalizacja napięć.
- Praca nad prawidłową funkcją MDM.
Należy mieć na uwadze, że bardzo często w procesie terapeutycznym potrzebujemy pracy w zespole interdyscyplinarnym, w którym swoje miejsce mają między innymi: ginekolog, seksuolog, psycholog, dietetyk czy urolog.
Piśmiennictwo
- Milsom I., Altman D., Cartwright R., Lapitan M.C.M., Nelson R., Sjöström S. et al.: Epidemiology of urinary incontinence (UI) and other lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), pelvic organ prolapse (POP) and anal (AI) incontinence. Paris 2013, ICUD-EAU, 15-107.
- Abrams P., Cardozo L., Fall M. et al.: The standardisation of terminology in lower urinary tract nction: report from the standardisation subcommittee of the International Continence Society. „Urology”, 2003, 61, 1, 37-49.
- Aoki Y., Brown H.W., Brubaker L., CornuJ.N., Daly J.O., Cartwright R.: Urinary incontinence in women. „Nat Rev Dis Primers”, 3, 2017, 17097.
- Minassian V.A., Yan X., Lichtenfeld M.J., Sun H., Stewart W.F.: The iceberg of health care utilization in women with urinary incontinence. „Int Urogynecol J”, 23, 2012, 1087-93.
- Bø K., Hagen R., Kvarstein B., Larsen S.: Pelvic floor muscle exercise for the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence: V. Female stress urinary incontinence and participation in different sport and social activities. „Scand J Sports Sci”, 11, 1989, 117-121.
- Dumoulin C., Adewuyi T., Booth J., Bradley C., Burgio B., Hagen S. et al.: Adult conservative management. 6th Ed. Abrams P., Cardozo A., Wagg A., Wein A. (eds.): Incontinence, Vol. 2. Committee 1, 2017, 1443-1628.
- Dumoulin C., Cacciari L.P., Hay-Smith E.J.C.: Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women. „Cochrane Database Syst Rev”, 10, 2018, 005654.
- Aoki Y., Brown H.W., Brubaker L., Cornu J.N., Daly J.O., Cartwright R. et al.: Urinary incontinence in women. „Nat Rev Dis Primers”, 3, 2017, 17097-26.
- DeSilva J., Rosenberg K.: Anatomia, rozwój i funkcja miednicy ludzkiej. „Anat Rec”, 2017, 300, 628-32.
- Baranowski W., Rogowski A.: Uroginekologa. Medical Tribune Polska, Warszawa 2018.
- Bordoni B., Sugumar K., Leslie S.W.: Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Pelvic Floor. StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA 2020.
- Park H., Han D.: Wpływ korelacji między skurczem mięśni dna miednicy a ruchem przepony podczas oddychania. „J Phys Ther Sci”, 2015, 27, 2113-5.
- Hodges P., Sapsford R., Pengel L.: Funkcje posturalne i oddechowe mięśni dna miednicy. „Neurourol Urodyn”, 2007, 26, 362-71.
- Stone C.: Osteopatia wisceralna i położnicza. MedPharm, Wrocław 2021.
- Wideman T.H., Scott W., Martel M.O., Sullivan M.J.: Recovery from depressive symptoms over the course of physical therapy: a prospective cohort study of individuals with work-related. „Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy”, 2012, 42, 11.
- Bergeron S., Reed B.D., Wesselmann U., Bohm-Starke N.: Vulvodynia. „Nat Rev Dis Primers”, 2020, 6, 1, 36.
- Main C.J., George S.Z.: Psychologically informed practice for management of low back pain: future directions in practice and research. „Phys Ther”, 2011, 91, 5, 820-4.
- Worman R. et al.: Methods used to investigate tone of pelvic floor muscles in pelvic health conditions: A systematic review. „Continence”, 6, 2023, 100593.
- Laycock J.: Pelvic Floor Muscle Assessment: The PERFECT Scheme. „Physiotherapy”, 87, 12, 2001, 631-42.
mgr Joanna Piórek-Wojciechowska
Prywatna praktyka
Czytaj więcej > artykułów < tej autorki
mgr Joanna Piórek-Wojciechowska jest prelegentką podczas
>> IV Konferencji „Ból w praktyce fizjoterapeuty” <<

Mogą zainteresować Cię również
Wywiady
„Empatia i doświadczenie – fundament pracy fizjoterapeuty sportowego”. Rozmowa z Wojciechem Hermanem
Jak dużą rolę w profilaktyce urazów odgrywa współpraca między fizjoterapeutami, trenerami przygotowania motorycznego i sztabem medycznym? To na pewno bardzo ważny element, ale nigdy nie uchronisz całej grupy zawodników przed urazami. W obecnych czasach, gdy dynamika gry jest bardzo duża, urazy niestet...